前段时间业务上有一个需求,这个需求需要查询数据库,由于单表数据比较大,导致出现超过5s的慢查询。随后,为了快速修复慢查询对整个系统带来的影响,将查询的数据源通过简单粗暴的修改配置切换到从库上。此后,增加了memcached来缓存一些case下的查询数据,但是对从库配置实现方式,并没有去调整。
最近,有其他业务的数据查询也需要切换到从库上,因此对上述简单的配置实现进行了思考。
动态数据源,其实就是根据我们的代码实现和配置来选择不同的数据源进行sql操作。一般地,我们会把读操作移到从库中,从而减轻主库的压力,也就是所谓的读写分离。
当然,对于一些使用数据库中间件来完成读写分离,而不需要业务层来做。这种方式,在大互联网公司中大量使用,比如360基于mysql-proxy的Atlas,阿里的DRDS(基于淘宝之前开源的TDDL)以及网易的分布式数据库中间件DDB等等。
对于一些未使用部署数据库中间件的公司,简单的方法就是在代码里面使用AOP方式通过对每个DAO层sql请求进行配置,来完成自定义的动态数据源。
Spring提供了一个抽象类AbstractRoutingDataSource,该类可以让开发人员快速实现数据源路由完成根据不同请求使用不同数据源的需求。
AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类,继承关系如下图:
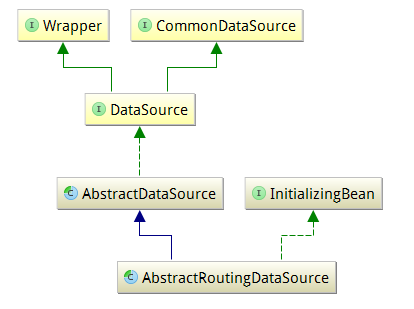
Notes: 抽象类最终继承javax.sql.DataSource类,该数据源类提供的一些接口就是我们最终需要实现的。
DataSource接口主要提供了两个方法给开发者实现,因此实现动态数据源,我们只需要把这两个方法的实现,在调用数据库查询的时候,告知执行上下文,运行环境拿到对应的数据库连接,就可以连接到对应的数据库进行查询更新等操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public interface DataSource extends CommonDataSource,Wrapper {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
Connection getConnection(String username, String password)
throws SQLException;
}
|
解析来,需要分析Spring提供给我们的抽象数据源路由类。既然AbstractRoutingDataSource简化了大家实现动态数据源功能的开发工作,那么该类必然会实现DataSource的两个接口方法。其需要决定,在什么情况下,使用哪个数据源的Connection连接。
AbstractRoutingDataSource怎样来获取数据源连接呢?
使用Map数据结构存放所有配置中使用的数据源,value是数据源DataSource对象,key则是根据我们自己的爱好来取名的,比如:master,slave等。这样,我们可以根据具体Dao方法配置的数据源key来获取对应的DataSource对象,从而告知运行环境该sql查询使用哪一个connection连接。
下面给出AbstractRoutingDataSource的部分实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
private boolean lenientFallback = true;
private DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup = new JndiDataSourceLookup();
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources) {
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
}
public void setDefaultTargetDataSource(Object defaultTargetDataSource) {
this.defaultTargetDataSource = defaultTargetDataSource;
}
public void setLenientFallback(boolean lenientFallback) {
this.lenientFallback = lenientFallback;
}
public void setDataSourceLookup(DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup) {
this.dataSourceLookup = (dataSourceLookup != null ? dataSourceLookup : new JndiDataSourceLookup());
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.targetDataSources == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required");
}
this.resolvedDataSources = new HashMap<Object, DataSource>(this.targetDataSources.size());
for (Map.Entry entry : this.targetDataSources.entrySet()) {
Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(entry.getKey());
DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(entry.getValue());
this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource);
}
if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null) {
this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource);
}
}
protected Object resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object lookupKey) {
return lookupKey;
}
protected DataSource resolveSpecifiedDataSource(Object dataSource) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (dataSource instanceof DataSource) {
return (DataSource) dataSource;
}
else if (dataSource instanceof String) {
return this.dataSourceLookup.getDataSource((String) dataSource);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal data source value - only [javax.sql.DataSource] and String supported: " + dataSource);
}
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
}
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
}
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
}
|
3.1 实现抽象路由数据源类
上一节介绍了抽象类AbstractRoutingDataSource,继承这个抽象类,我们实现动态数据源,只需要告诉抽象类,当前使用哪个key去获取数据源(determineCurrentLookupKey)。
在项目中,我们一般会指定哪些数据库操作需要使用哪个数据源,这个设置会存放在上下文中。也就是,我们可以使用ThreadLocal来存放当前数据操作使用的key。
因此,可以实现两个类,一个类实现AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象接口;一个来获取当前上下文中对应的key值。代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceHolder.getDataSource();
}
}
public class DynamicDataSourceHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> dsHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static String getDataSource() {
return dsHolder.get();
}
public static void putDataSource(String value) {
dsHolder.set(value);
}
public static void clear(){
dsHolder.remove();
}
}
|
通过上面两个类,我们就可以从上下文中获取当前操作需要使用的key值,然后通过实现的抽象路由数据源类来找到配置的DataSource,这样spring上下文就知道具体使用哪个connection连接来操作数据库sql了。
Tips: 这里需要注意ThreadLocal类中实现了clear方法,主要是在一个线程中会存在多个sql操作,可能设计不同的数据源,如果不清除当前sql的数据源,可能接下来的sql操作也会使用前一个操作设置的数据源连接,导致错误。
3.2 实现AOP简化配置
上一小节完成了怎样从上下文中获取设置的key,从而使用哪个数据源连接。但是,如何告知哪些操作使用哪个数据源key。
我们可以在每个需要使用动态数据源的地方,在具体业务代码的开始,把key值put到线程上下文中;然后在业务代码结束的地方,把上下文的设置清除掉。这样可以完成我们的需求,但是,对业务代码的侵入程度有点大哦。
上述这种场景,非常适合使用AOP技术完成。关于AOP介绍,可以参考:http://oss.org.cn/ossdocs/framework/spring/zh-cn/aop.html
采用AOP技术,我们需要在配置文件(或注解方式)中设置切点pointCut,然后我们需要实现切点前调用的方法(threadLocal中存入数据源key),和切点后调用的方法(清除threadLocal数据)。
为了使用方便,我们使用注解的方式配置数据源key。注解的实现代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface DBSource {
String value();
}
|
接下来,看看怎样实现AOP的before和after通知方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| public class DataSourceAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataSourceAspect.class);
public void before(JoinPoint point) {
Object target = point.getTarget();
String method = point.getSignature().getName();
Class<?>[] classz = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ((MethodSignature) point.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterTypes();
try {
Method m = classz[0].getMethod(method, parameterTypes);
if (m != null && m.isAnnotationPresent(DBSource.class)) {
DBSource data = m.getAnnotation(DBSource.class);
DynamicDataSourceHolder.putDataSource(data.value());
logger.info("-------数据源:{}------",data.value());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("=======================AOP注册拦截失败了!",e);
}
}
public void after(JoinPoint point){
Object target = point.getTarget();
String method = point.getSignature().getName();
Class<?>[] classz = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ((MethodSignature) point.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterTypes();
try {
Method m = classz[0].getMethod(method, parameterTypes);
if (m != null && m.isAnnotationPresent(DBSource.class)) {
DynamicDataSourceHolder.clear();
logger.info("-------清除ThreadLocal------");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("=======================AOP注册拦截失败了!",e);
}
}
}
|
这样,我们接下来,只需要在xml文件中配置相关切点和通知方法,即完成了整个动态数据源功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="dataSourceAspect" class="io.github.ketao1989.simple.service.dataSource.DataSourceAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="dsa" ref="dataSourceAspect">
<aop:pointcut id="pc" expression="execution(* io.github.ketao1989.dao.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="pc" method="before"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="pc" method="after"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
|
本文的代码和spring源码注释可以在github上查看:
Spring源码注释:https://github.com/ketao1989/cnSpring
spring 动态数据源项目:https://github.com/ketao1989/simpleSpringProject
最后,本文借鉴参考了博客园中的一篇博客:spring实现数据库读写分离。感谢!
